What are AI Agents?
AI agents represent a powerful new form of automation, merging the precision of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) with the cognitive power of Large Language Models (LLM). While RPA handles repetitive, rule-based tasks, LLMs provide the agent with language comprehension, decision-making, and contextual adaptation. This synergy allows AI agents to process both structured and unstructured data, automate complex workflows, and integrate with traditional AI models to offer predictive and prescriptive insights.
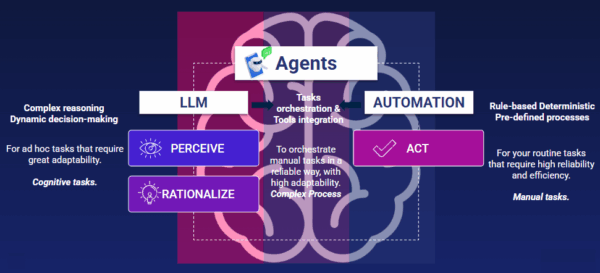
AI agents function like highly capable assistants, automating tasks while simultaneously learning from data to enhance decision-making and boost productivity across the organization.
AI Agents in the Retail Ecosystem
Considering the complexity of the retail scenario, AI agents offer a versatile solution that impacts every stage of the value chain:
- Marketing: Scaling hyper-personalization campaigns, developing customized assets and optimizing investment efficiency.
- Supply Chain: Enhancing stock management and logistics, reducing stockouts, and supporting in-store restocking.
- Operations: Providing insights to optimize store and e-commerce performance and the overall customer experience.
- Customer Service: Automating interactions to improve service delivery, reduce costs, and increase satisfaction.
Several retailers are already embracing the power of the agentic wave. Walmart, for example, is using AI agent systems with computer vision and shelf sensors for autonomous inventory management, enabling real-time stock monitoring. This intelligent agent triggers restocking orders when stock drops, which effectively reduced out-of-stock events by 30% in pilot stores, significantly cutting labor costs and accelerating the replenishment process. Similarly, DSW (North American footwear retailer) implemented an AI chat agent for customer service that handles complex tasks like authentication, exchanges, and returns, resulting in annual savings of $1.5 million and boosting shopper engagement by 60%2.
These examples highlight the immediate benefits of applying single AI agents to specific processes. However, the true transformation lies in moving beyond these isolated use cases to a more coordinated, system-wide approach. The future involves designing multiple specialized AI agents that work together, each handling a distinct part of a core function workflow rather than solving single, disconnected problems. This collaborative model unlocks greater efficiency and strategic value across the organization.
This coordinated environment is defined as an Agent Space —a role-based workspace where agents share data, context, and tools to observe, reason, act, learn, and escalate when necessary. By connecting directly to core systems like ERP, WMS, and CRM, an Agent Space streamlines daily operational tasks while also generating strategic insights. This fundamental shift redefines the role of retail teams, transitioning them from manually managing processes to guiding decisions, strengthening relationships, and focusing on innovation, using the collective intelligence of the agents.
Agentic AI Spaces: A New Operating Model
To better illustrate the concept of Agent Spaces, let’s dive into their application and impact on one of the retail industry’s core functions: Category Management, responsible for critical activities such as product assortment, pricing strategies, promotions, and supplier relationships. These high-impact tasks can be supported by an Agent Space, where a coordinated set of AI agents work together to continuously analyze demand, monitor competition, simulate scenarios, recommend the next best actions, and execute changes seamlessly across core systems.
Key Agent Examples:
Negotiation Co-Pilot Agent: This agent acts as a proactive assistant for category managers, focused on streamlining tasks and enhancing strategic decision-making. Key functions include:
- Automation: It automates data integration and reporting, consolidating real-time sales and inventory data, and helps organize activities by managing task prioritization and contract renewal reminders with summaries.
- Strategic Insights: It facilitates hypothesis testing via an interactive chatbot for “what-if” scenario modeling (like price adjustments), recommends the key talking points to be covered during the negotiation, provides proactive insights on underperforming products, and uses AI-Driven Forecasting to predict future demand and inform pricing and stock strategies.
Intelligent Assortment Agent: This agent analyzes the current product portfolio and identifies opportunities for innovation and performance maximization:
- Monitoring and Strategy: It continuously tracks product performance, analyzes emerging market trends, and supports the creation of a dynamic assortment strategy that adapts to changing customer preferences and competitor movements in real-time.
- Optimization: It provides Planogram Insights and Optimization by leveraging data to recommend product placement in-store and online, considering customer behavior and shelf efficiency.
A successful real-world example is H&M, which used an agentic AI solution to monitor customer movements and purchase patterns via sensory data. Based on these insights, the system recommends optimized product placements and layout designs, leading to a 17% rise in their average basket size and faster layout iterations without needing additional staff.
This agentic shift redefines the Category Manager’s role, moving their focus from reactive, manual effort (data collection, reporting) to proactive, strategic vision (market opportunity, high-level relationship management). They evolve from data aggregators to strategy accelerators.
Agentic Commerce: The Future of Shopping with AI Agents
AI agents are not just transforming back-end operations; they are directly shaping how consumers shop. This shift is driving Agentic Commerce, where AI-driven experiences redefine the consumer-retailer relationship.
Agents are becoming active participants in the shopping journey, autonomously browsing products, comparing prices, and offering highly tailored recommendations. Studies show that shoppers who interact with AI agents are 10% more engaged and have a 27% lower bounce rate. By learning from past interactions, these agents evolve with the shopper’s preferences, acting as trusted guides.
Agentic Commerce is a fundamental reshaping of online shopping. It replaces traditional click-and-search behavior with an integrated, intent-driven flow that orchestrates frictionless, personalized journeys. The scale of this shift is massive: the U.S. B2C retail market alone could see up to $1 trillion in AI-orchestrated transactions by 2030.
Overcoming Challenges: How to Begin Integrating AI Agents
Retailers don’t need perfect data maturity to start. Successful integration is built on establishing the right foundational enablers across four core layers:
- Trust Layer: Ensures security, compliance (e.g., LGPD), and transparency.
- Intelligence Layer: Houses AI models, prompt libraries, and orchestration models needed for business tasks.
- Data Layer: Effective management of structured and unstructured data for informed decision-making.
- Infrastructure Layer: A robust, scalable foundation to support AI applications and integrations.
With these pillars in place, the first phase of implementation should prioritize clear, measurable ROI to both demonstrate value and fund broader transformation. Retailers can start by:
- Identifying High-Friction Workflows: Focus on repetitive, time-consuming activities like Tier 1 customer support or stock-level monitoring, where agents can quickly reduce workload and costs.
- Launching Goal-Oriented Pilots: Deploy targeted agents tied to specific KPIs (e.g., resolution time, conversion uplift). Proven examples, like Walmart’s automated replenishment, demonstrate how small, well-scoped pilots unlock significant efficiency gains and set the stage for scaling.
Conclusion: Getting Ready for the Future
AI agents are more than just an efficiency tool; they are a core strategic capability that will define the next era of retail. From optimizing internal workflows to driving Agentic Commerce, their impact spans the entire retail ecosystem. Retailers who embrace this shift will unlock significant gains in productivity, personalization, and customer loyalty.
Successful adoption requires a strategic, phased approach. By empowering teams, rethinking processes, and designing consumer experiences around intent, retailers can convert this technological transformation into a decisive competitive advantage. The industry is shifting — and the retailers who act now will be the ones who define what comes next.

 BLOG
BLOG







