The story so far: From matching to reasoning
- Early foundations (1998–2015): Ranking and matching defined Google’s early years. Updates like Panda and Penguin pushed the ecosystem towards relevance-focused ranking and content quality. Their massive database, Knowledge Graph, shifted search from string-matching to entity recognition. The launch of E-A-T (Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) emphasized the importance of credible, accurate, and trustworthy content, while RankBrain introduced machine learning into ranking.
- The neural leap (2017–2019): Google’s Transformer architecture enabled semantic understanding and laid the foundations of modern LLMs. Google’s BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) helped parse nuance in queries, moving search even closer to language comprehension.
- Platform diversification (2010–now): As user behavior shifted to more prevalent use of social media, discovery expanded across YouTube, TikTok, Reddit, and Pinterest, each with unique audiences and trust signals.
- The generative shift (2022–2023): With OpenAI’s launch of ChatGPT, generative AI entered search. Bing integrated GPT; Google launched Bard and AI Overviews. Search began to “talk back.”
- The AI-first SERP (2024–2025): AI Mode and Overviews reconfigured SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages) into a conversational workspace, where reasoning and synthesis matter more than rank.
“AI has been shaping search for years, but the type, scale and speed of change we’re seeing now is different. It’s not just about new technology; it’s a redefinition of how, where, and why people search, and how search operates.” – Charlie Kay
How LLMs (large language models) work and impact search
Large language models, or LLMs, are the brains behind ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude, and every chatbot or AI-powered summary you’ve seen appear in search engines recently. They learn patterns in language from this documentation and use that knowledge to:
- Understand natural language queries,
- Generate fluent, human-like responses,
- Summarize or rephrase content,
- Infer relationships between words, concepts, and ideas.
LLMs are trained on vast datasets, tokenized into mathematical patterns. They generate text by predicting tokens or series of tokens, sometimes augmented by retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), which blends static knowledge with real-time sources.
Unlike traditional search, LLMs don’t just crawl the web to fetch results; they build answers, often reasoning step by step. Visibility now depends on being structured, accessible, and “reasoning-ready.”
Google launches AI Overviews and AI Mode
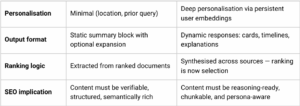
SEO once focused on optimizing pages for a query, but with generative search we now have to optimize for a space that is hyper personalized, intent-first, multi-query, and reasoning-driven. AI Overviews and AI Mode are built and work differently to traditional Google search.
- AI Overviews: Extractive summaries are embedded in SERPs, rephrasing content with citations. Impressions rise but clicks fall as answers appear directly in the SERP.
- AI Mode: A full-screen conversational experience, AI Mode uses query expansion, reasoning traces, and paragraph-level comparisons, building answers dynamically. Content isn’t ranked but judged.
Together, they mark a new logic: from keywords to intent clusters, rankings to reasoning, clicks to citations.
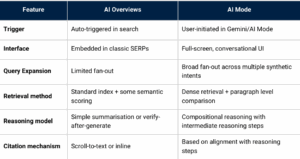
AI Mode vs. AI Overviews: A side-by-side comparison
AI search: Who’s adopting it?
Although AI search remains limited, it’s growing fast. Less than two percent of organic traffic currently comes from AI-driven searches, though referral traffic is rising sharply. ChatGPT and Perplexity dominate AI referrals, with adoption strongest among younger, digitally fluent audiences. Traditional search still rules, but the trajectory is clear.
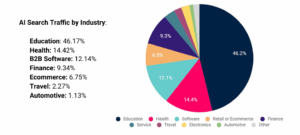
AI Assistants: Which are being used most?
Despite the fact that AI platforms only make up a fraction of total digital usage, they’re undoubtedly growing, and there are leaders in this race.
A SparkToro x Datos State of Search Report shows that ChatGPT has become the dominant AI assistant globally, making the Top 5 destinations visited from traditional search engines in both the U.S. and Europe – owning ~30% AI share. A recent study by SEMRush even indicates that ChatGPT is actually expanding the way people seek information.
According to research, 63% of ChatGPT users are under 34 years of age, meaning that Millennials and Gen Z are the biggest user groups, many of whom are daily users. Only 13% of ChatGPT users are 55 or older and just five percent are 65+.
What these stats mean for marketers and brands
There are new metrics for influence and visibility. While traditional SEO metrics still matter in specific circumstances, the metrics that are reported on need to adapt and change. Here is a list of what brands and marketers need to do:
- Deep audience research: Move beyond keywords to forums, reviews, and social data.
- AI visibility and measurement: Track citations, mentions, and zero-click influence, not just rankings.
- Tailor strategy to platform: Optimize differently for Gemini, Copilot, Perplexity, and ChatGPT.
- Brand building and PR: Mentions and authority are critical signals for AI inclusion.
- Reputation and trust: Structured, factually clear content aligns with E-E-A-T principles.
- Semantic and structured optimization: Schema and clarity aid machine retrieval.
- Multimodal content: Optimize across text, images, video, and audio.
- Content architecture: Create modular, “chunkable” content that AI can use.
- Crawlability and agent access:Ensure assistants can access feeds and APIs.
- Feedback and monitoring: Track how AI tools cite and use your content.
- Agentic readiness: Prepare for AI-led transactions where assistants handle purchase flows.
Final takeaways – and a look forward
Both traditional search and AI search are growing: some studies predict AI search will surpass traditional search by 2028.
New research suggests that 20% of Americans use AI tools 10x per month. Google’s AI Mode and Overviews are changing behaviours, and adoption will accelerate. For now, traditional SEO still underpins AI visibility: ranking well correlates with citation in AI outputs.
This isn’t the demise of SEO but its evolution. Marketers must shift from optimizing for rankings to optimizing for reasoning, aiming for inclusion and influence in AI-generated answers. Brands that thrive will combine fundamentals such as strong products, authentic storytelling, genuine customer understanding with adaptation to AI’s new search logic.
“The brands that will win in this new ecosystem are those that stay visible across platforms, structure their content for both human and machine readability, evolve their measurement frameworks, and consistently prioritise real value, trust, and usability. The future of search is layered, multimodal, and agentic — and the time to get ready is now.” – Charlie Kay

 BLOG
BLOG






