El SEO y los canales SEA son componentes clave en la combinación de marketing digital para la mayoría de las empresas, pero a menudo falta una estrategia de marketing conjunta.
El director de SEA no sabe lo que hacen sus colegas de SEO, y viceversa. ¿Le ocurre lo mismo a usted? Entonces se enfrenta al reto de relacionar estos temas.
En nuestro primer artículo sobre Full Search, "SEO & SEA synergy: myth or reality", de Elodie Descatoire y Thomas Quélin, el tema de Full Search se desglosa en los aspectos de análisis de marketing, análisis técnico y análisis de rendimiento, ofreciendo al lector una sencilla introducción al tema. A partir de ahí, este artículo presenta casos de uso concretos que dan una idea de cómo puede enfocarse operativamente la Búsqueda Completa en el trabajo diario.
En primer lugar, este artículo aborda la delimitación de los canales SEO y SEA y cómo pueden combinarse de forma rentable en un enfoque de búsqueda completa. A continuación, mediante casos de uso detallados de búsqueda completa, se presentan diversos casos de uso en los que las desventajas de un canal se compensan con las ventajas del otro y, en última instancia, los recursos y el presupuesto se utilizan de forma eficiente.
Diferencias entre los canales SEO y SEA
La optimización para motores de búsqueda (SEO) y la publicidad en buscadores (SEA) se distinguen claramente entre sí. Sin embargo, dado que ambos tienen lugar en las páginas de resultados de búsqueda (SERPs), siempre tiene sentido considerarlos conjuntamente.
Anuncios de pago
Los anuncios SEA de pago marcados como tales por la referencia "ad". Los anuncios de compra también contienen este tipo de denominación. La colocación de los anuncios se realiza según el sistema de subasta con facturación, que funciona mediante un método de coste por clic. Así, el anunciante incurre en costes por cada clic en los anuncios.
Las medidas de EAE pueden crear visibilidad a corto plazo para un dominio, que puede verse en forma de anuncios de EAE por encima de los resultados de búsqueda orgánica en el campo visual directo de los usuarios.
Pueden crear valor adicional para los usuarios mediante extensiones de anuncios especiales. Además, los gestores de EAE tienen un amplio control sobre los textos y las extensiones de anuncios. Es posible realizar análisis específicos de campañas individuales, anuncios o palabras clave.
Fragmentos orgánicos
El área bajo los anuncios SEA incluye los llamados resultados orgánicos de búsqueda. Estos pueden mostrarse en diferentes variantes. Ya sea como resultado de búsqueda normal, también llamado snippet, como rich snippet o como featured snippet. La ubicación de los fragmentos orgánicos viene determinada por el ranking de la URL para la palabra clave buscada. La posición en el ranking de la URL está influenciada por varios factores que pueden cambiar con cada actualización del algoritmo de Google. Al igual que SEA, el canal SEO tiene sus propias ventajas. Un sitio web optimizado para SEO conlleva una mayor visibilidad a largo plazo gracias a una mejor capacidad de búsqueda en las SERP, así como el consiguiente tráfico del sitio web. Los usuarios escépticos ante los anuncios o que no los ven debido a un bloqueador de anuncios también hacen clic en la búsqueda orgánica.
Enfoque de búsqueda completa
Aunque ambos canales, SEO y SEA, tienen lugar en los resultados de búsqueda y ofrecen respuestas a las consultas de búsqueda de los usuarios, en realidad suelen considerarse por separado.
Sin embargo, existe un gran potencial para aprovechar plenamente las ventajas y desventajas de cada canal mediante una orientación estratégica conjunta en forma de enfoque de búsqueda completa.
Un enfoque de búsqueda completa considera ambas áreas de la mano, garantizando así una cobertura óptima de las SERP y creando así una mayor visibilidad y un rendimiento más sólido con un uso eficiente del presupuesto.
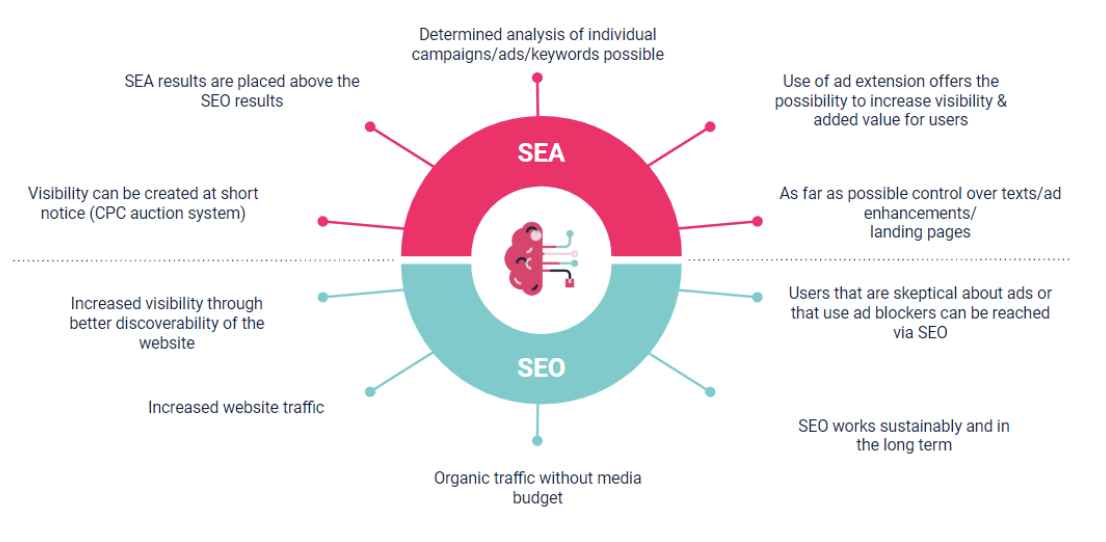
Figura 1: SEO y SEA van de la mano: Una cobertura óptima de las SERP y la creación de visibilidad y rendimiento requieren un sólido enfoque de búsqueda completa
¿Por qué necesitamos un enfoque de búsqueda completa?
En la práctica, suele haber un solapamiento de los enfoques de optimización y un mayor uso del presupuesto y los recursos, ya que los canales se optimizan por separado. Debido a la optimización por separado de ambas áreas, es muy posible que los responsables de SEO y SEA optimicen las mismas palabras clave y que los recursos y el presupuesto no se utilicen de forma óptima.
Combinando ambos canales en un enfoque de búsqueda completo, se pueden conseguir optimizaciones a corto, medio y largo plazo.
Debido a la creciente presión competitiva y al aumento de los CPC en SEA, también es cada vez más necesario utilizar el presupuesto de la forma más eficiente posible. Por lo tanto, debe utilizarse un enfoque de búsqueda completa.
Casos prácticos de búsqueda completa
Los casos de uso de búsqueda completa pueden encontrarse en cualquier punto del recorrido del cliente. Dependiendo del paso del embudo, se pueden utilizar diferentes casos, que los usuarios pueden encontrar en diferentes fases del recorrido del cliente. A continuación, se describen algunos casos de uso y soluciones que subrayan la importancia de un enfoque de búsqueda completa.
Mejorar la visibilidad
La mejora de la visibilidad debe lograrse mediante el uso de medidas coordinadas de SEO y SEA. El objetivo es presentar el propio Compañia de la forma más destacada posible en las páginas de resultados de búsqueda de Google. Esto puede lograrse mediante el denominado efecto de listado múltiple, en el que Compañia aparece en la sección de anuncios de Google y en los resultados de búsqueda orgánicos. El listado múltiple de la marca aumenta la percepción de la misma y conduce a una mayor confianza del cliente en la marca. Este caso se utiliza con especial frecuencia para las palabras clave de marca.
Para el canal SEA, es aconsejable pujar por la marca propia, ya que, además de las ventajas ya mencionadas, como la impresión de alta calidad de la marca y la confianza, la competencia impide estar presente en los anuncios únicamente por estas palabras clave relativamente baratas y al mismo tiempo de alto tráfico para interceptar a los usuarios. Además, la probabilidad de conversión es mayor cuando los usuarios buscan directamente una marca, lo que también habla a favor de pujar por la marca propia.
En el canal SEO, es más difícil posicionarse en los primeros puestos para palabras clave genéricas. La clasificación para palabras clave de marca suele producirse automáticamente y rara vez requiere una estrategia de marca específica. En ambos canales, este caso para mejorar la visibilidad en las SERP es relativamente fácil y barato de aplicar, por lo que constituye la piedra angular de una estrategia de búsqueda completa.
Pruebas de meta data en SEA
Las optimizaciones SEO de metadatos como el título y la descripción siempre van de la mano para mejorar la clasificación orgánica, reforzar el tráfico del sitio web e, idealmente, aumentar la tasa de conversión. Dado que el rastreo y la indexación de los cambios en el contenido por parte de Google no tienen lugar inmediatamente, sino que siempre llevan algún tiempo, el contenido no debe cambiarse con demasiada frecuencia. El desarrollo del rendimiento también puede tardar unos días, por lo que no es posible determinar directamente si las optimizaciones tienen la influencia positiva esperada.
Para asegurarse de que los cambios en los metadatos conducen a una mejora del rendimiento, se pueden realizar pruebas a corto plazo en SEA con antelación. En función de los resultados, se evalúa entonces si tiene sentido un ajuste de los metadatos en SEO.
Para empezar la implementación, los módulos de texto se definen en la fase de prueba, teniendo en cuenta las restricciones de caracteres. A continuación, se seleccionan los grupos de anuncios adecuados con un volumen de tráfico suficiente y un periodo de prueba. Posteriormente, se crean pruebas A/B en forma de variaciones de anuncios, que se evalúan en términos de CTR y otros KPI de compromiso.
Utilizando este caso de búsqueda completa, gracias a la cooperación de ambos canales, se puede tomar una decisión establecida sobre cuándo tiene sentido la implementación de nuevos metadatos en SEO y cuándo no se materializará el aumento de rendimiento esperado.
Preparar eficazmente los contenidos para los fragmentos destacados
Una estrategia integral de búsqueda completa incluye la identificación de los puntos fuertes y débiles de cada uno de los canales para desarrollar medidas orientadas al éxito del marketing. La reciente actualización de contenidos útiles de Google subraya una vez más la importancia de los contenidos de alta calidad que responden a la intención de búsqueda de los usuarios. Especialmente en las búsquedas orientadas a la información, el canal SEA a menudo alcanza sus límites, mientras que el canal SEO puede rendir al máximo en este caso. El tercer Full Search Case persigue el objetivo de eliminar los puntos débiles del canal SEA mediante optimizaciones específicas en SEO con respecto a las consultas de búsqueda orientadas a la información, de modo que las empresas estén presentes en las SERP para todos los tipos de consultas de búsqueda si es posible y puedan así cubrir todas las fases del recorrido del cliente.
(Qué, Dónde, Por qué, Quién) no suelen estar cubiertas, o sólo parcialmente, por las medidas de EAE, pero con mayor frecuencia se responden en las SERP en forma de fragmentos destacados. Con los fragmentos destacados, Google ha desarrollado una forma de ofrecer información en las SERP de muchas maneras diferentes. Estos fragmentos destacados pueden, por ejemplo, reproducir respuestas a preguntas directamente en las SERPs como los llamados ceros de posición. Pueden mostrarse en forma de texto, vídeos, listas y tablas. Para que su sitio web sea considerado para los fragmentos destacados, el contenido debe prepararse en consecuencia. Los temas relevantes pueden identificarse a través de la investigación de palabras clave y luego crearse como contenido en forma de preguntas y respuestas. Para que Google muestre el contenido como fragmento destacado, las preguntas deben marcarse como etiquetas H y las respuestas deben ser breves y concisas. Además de los textos continuos, los puntos clave y las tablas también son adecuados como formatos de contenido.
Las consultas de búsqueda de información no son infrecuentes en el caso de productos o servicios que requieren una explicación. Por tanto, este enfoque de búsqueda completa es especialmente adecuado para las primeras fases del recorrido del cliente que aún no está orientado a la conversión. Si el usuario ya se encuentra en la fase de conversión, las consultas de búsqueda pueden responderse mediante anuncios SEA orientados.
Páginas de destino SEO y SEA
Este caso de búsqueda completa también aborda los diferentes tipos de consultas de búsqueda y su relevancia dentro de los pasos del embudo del recorrido del cliente. Como quedó claro en el caso anterior, los canales pueden servir mejor o peor a distintos tipos de consultas de búsqueda. Este caso de búsqueda completa tiene como objetivo captar a los usuarios de forma más eficiente mediante el uso de páginas de destino SEO y SEA separadas y continuamente optimizadas, así como satisfacer sus expectativas e intenciones de búsqueda de la mejor forma posible.
Mientras que el SEO cubre sobre todo las consultas de búsqueda informativas, el SEA es más adecuado para las consultas orientadas a la conversión. Esto también debería reflejarse en las páginas de destino. Las páginas de aterrizaje SEO se caracterizan por ser informativas y útiles para los usuarios que aún se encuentran en la fase de orientación. El uso de preguntas ((Qué, Dónde, Por qué, Quién) y contenido explicativo es muy adecuado para las páginas de aterrizaje SEO y el uso de fragmentos destacados en las SERPs. En cambio, las páginas de aterrizaje SEA son más transaccionales y contienen información menos detallada. El objetivo en este caso es llevar al usuario lo más cerca posible de la conversión y destacar únicamente los USP más importantes una vez más. Por tanto, las páginas de aterrizaje SEA sólo deben servir para palabras clave claramente orientadas a la conversión. La página de aterrizaje SEO debe posicionarse para todas las demás palabras clave en las SERPs. Al utilizar paralelamente páginas de aterrizaje SEO y SEA, debe asegurarse de no incurrir en canibalización de palabras clave. Para ello, las páginas de destino SEA deben estar provistas de una "etiqueta noindex" para que no se produzca una clasificación orgánica.
Este caso de búsqueda completa garantiza una mayor tasa de conversión a largo plazo, una mejora sostenible del ranking de anuncios y un uso más eficiente del presupuesto de medios.
Apoyo al relanzamiento del sitio web con anuncios de EAE
Mientras que los casos anteriores se centraban en la estrategia de palabras clave, el recorrido del cliente y el contenido, el siguiente caso de búsqueda completa aborda la aplicación específica de un relanzamiento. El relanzamiento de un sitio web siempre va acompañado de oportunidades y riesgos. El contenido trasladado debe ser rastreado e indexado de nuevo por Google, lo que puede provocar a corto plazo pérdidas de rendimiento y de posicionamiento en SEO. Este caso de búsqueda completa tiene como objetivo compensar temporalmente estas pérdidas de rendimiento relacionadas con el relanzamiento mediante el uso de campañas de SEA para evitar pérdidas de visibilidad y eficacia. En el caso de que ya se hayan tomado medidas de SEA, el esfuerzo inicial es bastante reducido. Aumentando el presupuesto y reservando palabras clave adicionales, se puede prestar apoyo a corto plazo. Si no se han tomado medidas de EAE hasta el momento, el esfuerzo inicial es mayor y requiere más tiempo de preparación.
Panel de búsqueda completo
El seguimiento es esencial para poder evaluar y ajustar las medidas adoptadas. El objetivo del último caso de búsqueda completa es, por tanto, crear un sistema de seguimiento correctamente diseñado, definir los KPI y los objetivos de conversión adecuados y utilizar la medición multicanal para supervisar el rendimiento. Para obtener una visión y una evaluación exhaustivas del rendimiento, se recomienda el uso de un cuadro de mando holístico de búsqueda completa. Además de data de Google Search Console, el informe de Google Ads "Paid and Organic" puede constituir una base sólida para una buena comparación data .
El impacto de los Casos de Uso de Búsqueda Completa enumerados, así como otras medidas, pueden hacerse visibles y medibles a lo largo del tiempo dentro del cuadro de mando. Dependiendo del uso y del grupo objetivo del cuadro de mando, los KPI deben decidirse individualmente.
Conclusión de los casos de búsqueda completa
Los seis casos mostraron cuánto potencial encierra un enfoque de búsqueda completa y cuántos frutos maduros pueden recogerse aquí. Ya se trate de la mejora de la visibilidad a través de efectos multi-listado, metadatos para pruebas previas en SEA, contenido optimizado para el uso de fragmentos destacados, páginas de destino SEO y SEA separadas para una mejor coincidencia de la intención de búsqueda, anuncios SEA que apoyan relanzamientos de sitios web o medición multicanal para supervisar el rendimiento en un panel de búsqueda completo.
Los casos presentados abordan temas diferentes, pero persiguen un objetivo común. Se trata de reconocer el potencial de los canales e integrarlos específicamente en una estrategia de búsqueda completa. La estrategia conjunta de búsqueda completa también evita la canibalización entre SEO y SEA.
Para poder aprovechar el potencial, hay que crear una conciencia interna de que existe algo más que el propio canal. ¿Hablan entre sí los responsables de SEO y SEA de su Compañia ? ¿Están alineadas las estrategias o se persigue una estrategia conjunta? Si no es así, el primer paso debería ser crear conciencia del otro canal y fomentar la comunicación y el intercambio. Mirar más allá del propio canal y descubrir nuevas oportunidades de sinergia son las bases de una estrategia de marketing de éxito.
La implementación de una estrategia de búsqueda completa no sólo garantiza el desarrollo de los empleados en términos de nuevas competencias en su propio canal, sino que también aporta beneficios muy claros para las empresas, como el aumento de la eficacia de las campañas y la minimización de los costes en el marketing mix. Revise sus procesos internos y su estrategia de marketing e inicie el camino hacia un enfoque de búsqueda completa.

 BLOG
BLOG






